Ever wondered how your favourite songs are crafted? Music production is the artistry that transforms ideas into polished tracks. Whether you’re just curious about how it all works or you dream of becoming a music producer yourself, our guide will help you understand the journey and give you practical steps to get you started.
- What is music production?
- Who is a music producer and what do they do?
- Music Producer vs. Recording Engineer: What's the difference?
- Essential stages of music production
- What equipment do you need for music production?
- How to become a music producer
- 10 tips to become a successful music producer
- Can you become a music producer without a degree?
- Is music production expensive?
- How long does it take to become a music producer?
- Learn more about music production with our free trial
What is music production?
Music production is the art and science of creating, recording, mixing, and mastering music tracks. It encompasses everything from the initial song idea to the final mastered track ready for distribution. A music producer plays a vital role in this process, acting as a project manager, creative director, and technical wizard all in one.
Who is a music producer and what do they do?
 A music producer oversees the music production process, working closely with artists to develop their sound, compose music, arrange sessions, and refine the final product. Their responsibilities include:
A music producer oversees the music production process, working closely with artists to develop their sound, compose music, arrange sessions, and refine the final product. Their responsibilities include:
Providing creative input on songwriting and arrangement
Managing recording sessions
Mixing and mastering tracks
For example, one of the most famous music producers in recent times, Dr. Dre, is well-known for his hands-on approach, often helping to shape the sound and direction of the albums he produces.
Music Producer vs. Recording Engineer: What's the difference?
 While a music producer focuses on the creative and logistical aspects of creating music, a recording engineer specializes in the technical side of recording sounds. The recording engineer ensures all technical equipment is correctly set up and optimized to capture the best possible recordings.
While a music producer focuses on the creative and logistical aspects of creating music, a recording engineer specializes in the technical side of recording sounds. The recording engineer ensures all technical equipment is correctly set up and optimized to capture the best possible recordings.
But you can be both: George Martin, often referred to as the "Fifth Beatle," was both a producer and an engineer. His technical expertise and creative input were instrumental in shaping The Beatles' innovative sound.
Essential stages of music production
 Let's take a more in-depth look at the stages of music production:
Let's take a more in-depth look at the stages of music production:
Songwriting:
This initial stage involves creating the core elements of a song: the melody, harmony, and lyrics. The songwriter(s) may start with an idea, a chord progression, a catchy hook, or even a lyrical theme. The goal is to compose a piece of music that resonates emotionally and artistically. This process often involves brainstorming, improvisation, and refining ideas until the song’s foundation is solid.
Arranging:
Once the song is written, arranging determines how the song will be structured and orchestrated. This includes deciding on the verses, choruses, bridges, and other sections of the song. It also involves choosing the instrumentation and how different instruments will be used throughout the track. Arranging helps to shape the dynamics and flow of the song, ensuring it maintains the listener’s interest and emotional impact.
Tracking:
Tracking, or recording, involves capturing the individual elements of the song in a studio setting. This can include recording vocals, guitars, drums, keyboards, and any other instruments used in the arrangement. High-quality recording equipment and techniques are used to ensure each part is captured clearly and accurately. Musicians may record multiple takes of each part to achieve the best performance.
Editing:
Editing is the process of refining the recorded tracks. This can include correcting timing issues (quantisation), adjusting the pitch of vocals (tuning), and comping (selecting the best parts of multiple takes). Editing ensures that the performance is tight and polished, removing any mistakes or inconsistencies while maintaining the song’s natural feel.
Mixing:
Mixing is where the individual recorded tracks are balanced and blended into a cohesive whole. This involves adjusting the levels, panning, equalisation (EQ), compression, reverb, and other effects for each track. The goal is to create a mix where all elements work together harmoniously, with each part contributing to the overall sound without overpowering others. Mixing can dramatically impact the song’s final sound and emotional impact.
Mastering:
Mastering is the final stage of the production process. It involves preparing the mixed track for distribution by ensuring it sounds good across all playback systems. This includes adjusting the overall loudness, applying final EQ and compression, and ensuring consistency across an album if applicable. Mastering also involves creating the final version of the track (the master) that will be used for duplication and distribution across various platforms.
What equipment do you need for music production?
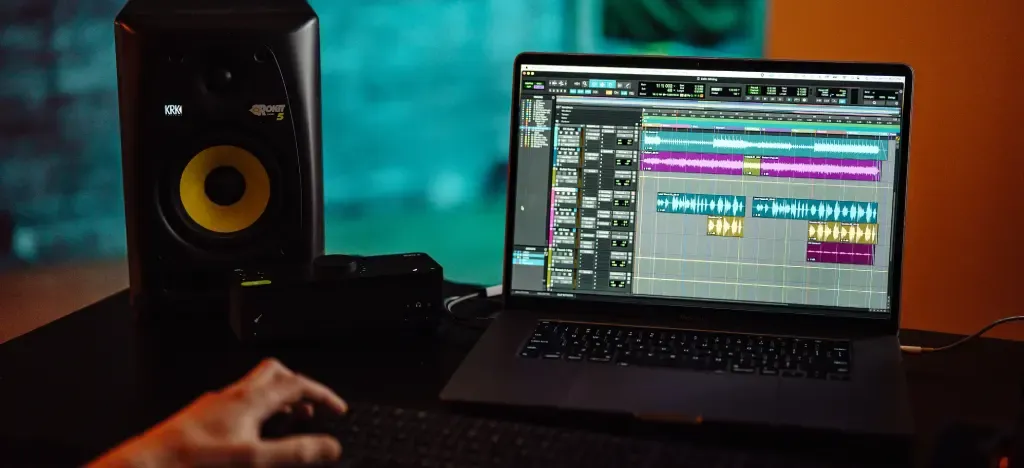
To start in music production, you'll need:
Personal Computer: A powerful computer to run your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) and other software.
Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): The software used for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering music.
Audio Interface: Converts analogue signals into digital form and vice versa.
Studio Monitors and Headphones: For accurate monitoring of your mixes.
MIDI Controller: To input musical notes and control software instruments.
Microphones: For recording vocals and acoustic instruments.
Deadmau5, a renowned electronic music producer, often shares his studio setup on social media, showcasing how he uses various DAWs, MIDI controllers, and other equipment to create his tracks.
How to become a music producer
 Becoming a music producer involves a combination of education, practical experience, and networking. Here are a few tips to get you started:
Becoming a music producer involves a combination of education, practical experience, and networking. Here are a few tips to get you started:
Explore Music: Listen to a wide variety of music and understand different genres.
Learn an Instrument: This provides a fundamental understanding of music theory and composition.
Education: Consider taking music production courses or pursuing a degree in music technology.
Get Practical Experience: Start creating your own music using a DAW to apply what you've learned.
Internship: Gain hands-on experience and industry insights through internships at studios or music companies.
Network: Build connections with industry professionals, attend music events, and engage with online communities.
Develop Your Portfolio: Create and refine a portfolio of your work to showcase your skills and style.
Remember, every great producer started from scratch. Through consistent effort and learning, you can build a successful career in music production.
► ARTMASTER TIP: Make a start by learning an instrument with ArtMaster's FREE 7-Day Trial.
10 tips to become a successful music producer
Discover the secrets to success in music production with these 10 invaluable tips:
Embrace Practice: Improving as a music producer requires continuous practice and exploration of new techniques.
Set Realistic Expectations: Focus on gradual improvement rather than perfection.
Accept Imperfection: Recognize that every great artist started with less-than-perfect works.
Prioritize Quantity for Growth: Create a volume of work to hone your skills and discover your unique style.
Seek Inspiration from Everywhere: Use resources like tutorials, blogs, and templates for inspiration.
Utilize Tools and Resources: Leverage loops, MIDI packs, and other resources to spark creativity.
Learn to Finish Projects: Develop the discipline to complete your tracks.
Make Decisive Moves: Avoid getting stuck on minor details; make decisions and keep the momentum going.
Regular, Consistent Practice: Commit to a regular schedule of music production, even if it’s just a small amount of time each day.
Enjoy the Process: Focus on the joy of creating music rather than the outcomes.
Can you become a music producer without a degree?
Yes, many successful music producers are self-taught and have built their careers through practical experience, networking, and continuous learning. However, formal education can provide valuable knowledge and opportunities.
Alex Moukala, an Italian-born orchestral composer and music producer, started his career without any formal music training. He learned music production through online tutorials and has since worked on Hollywood movie trailers and viral video game music remixes.
► ARTMASTER TIP: Take advantage of Alex's wealth of experience and expertise by taking in his beginner's course on Orchestral Music Production.
Is music production expensive?
Starting can be relatively affordable, especially with home studio setups. However, costs can increase with professional equipment, software, and further education. Remember, many successful producers started with a basic setup and gradually invested in more advanced tools as they progressed.
How long does it take to become a music producer?
The timeline to becoming a successful music producer varies widely. It can take several years of learning, practising, and networking to establish yourself in the industry. Although some producers, such as Max Martin (Britney Spears) and Pharrell Williams achieved major breakthroughs within just a few years. Just remember that every small project and collaboration brings you closer to your big break. Stay focused, keep creating, and persistence and passion might turn your dreams into reality faster than you think.
Learn more about music production with our free trial
Start your journey into music production with our free trial. Explore our courses, resources, and tools designed to help you succeed in the exciting world of music production.
Try Our FREE 7-Day Trial!


